My Therapy
options
Find the solution that best fits
your lifestyle and your health
When kidney failure reaches an advanced stage, it becomes essential to choose a treatment to replace kidney function. Each option has its own specifics and adapts differently to the patient’s needs, preferences, and health condition.
It is important to be well informed in order to make an informed decision with the support of your nephrologist.
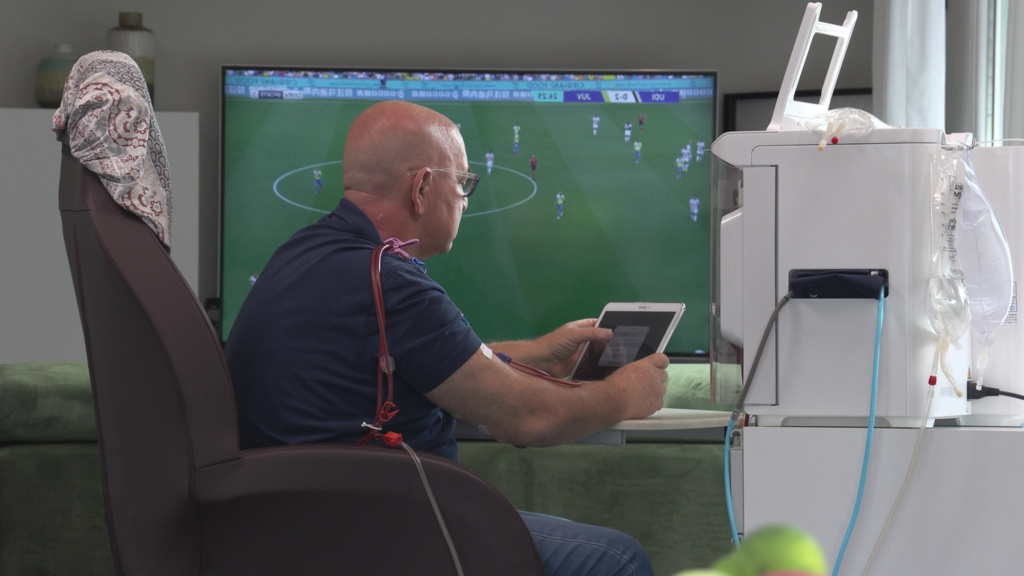

HOME DIALYSIS : MORE AUTONOMY EVERYDAY
La dialyse à domicile permet aux patients de réaliser leur traitement dans leur environnement familial, à leur rythme.3 Deux types de dialyse sont possibles à domicile :
Home hemodialysis
Home hemodialysis is based on the same principle as in-center dialysis. One variation is short and frequent home hemodialysis (5 to 6 times per week), which allows for more regular toxin removal and reduces post-dialysis fatigue.3
- Benefits (of frequent hemodialysis)3 :
+ More freedom to organize your schedule.
+ Fewer dietary and fluid restrictions.
+ Fewer abrupt changes in blood volume, reducing the risk of hypotension and cramps.
- Drawbacks9 :
– Requires training and regular medical follow-up.
– Minimal home adjustments may be required.
Peritoneal dialysis
This type of dialysis uses the peritoneum (the natural membrane of the abdomen) as a filter to remove waste and excess fluids. It is often performed continuously, either manually during the day (Continuous Ambulatory Peritoneal Dialysis – CAPD) or automatically at night using a machine (Automated Peritoneal Dialysis – APD).20
- Benefits21:
+ Gentle technique.
+ Can be done by autonomous patient after training.
+ Flexible in terms of scheduling, especially with nocturnal APD.
- Drawbacks9:
– Risk of peritoneal infection (peritonitis) if hygiene rules are not strictly followed.
– Less suitable for patients who have undergone multiple abdominal surgeries.
Medical support and comprehensive training ensure a smooth and confident transition to home dialysis.
DIALYSE EN CENTRE : UNe alternative encadrée
Pour les patients préférant être pris en charge par une équipe soignante, la dialyse en centre est une solution alternative.20 Elle peut se dérouler dans différents environnements :
- Dialysis center
- Satellites units
- Self-care units
It is performed three times a week in one of the specialized facilities mentioned, under the supervision of healthcare professionals. Each session lasts about 4 hours.
- Benefits20:
+ Constant medical supervision and safety.
+ Care is provided by the medical team.
+ No logistical or technical management required from the patient.
- Drawbacks20:
– Frequent travel to the dialysis center.
- Post-dialysis fatigue.
– The two consecutive days without dialysis can be physically taxing on the body.
LA TRANSPLANTATION RENALE : LA SOLUTION LA PLUS PROCHE DU FONCTIONNEMENT NATUREL
Kidney transplant is the solution that allows for near-normal kidney function. It involves replacing a failing kidney with a healthy kidney from a living or deceased donor.21
- Benefits21 :
+ Significant improvement in quality of life.
+ More freedom and fewer medical constraints.
+ Better life expectancy than with dialysis.
- Drawbacks21 :
– The wait for a transplant can be long.
– Requires lifelong immunosuppressive treatment to prevent organ rejection.
– There are risks of complications (rejection, infections).
An ideal solution for eligible patients, although access depends on many medical criteria.

TRAITEMENT CONSERVATEUR : UN CHOIX CENTRé SUR LA QUALITE DE VIE
Conservative care is a palliative option for patients who cannot undergo dialysis or transplantation. The goal is to slow the progression of the disease and relieve symptoms through appropriate care.21
Principles of conservative care21 :
- Symptom management and prevention of complications.
- Comprehensive care with medical and psychological follow-up.
- Personalized support to maintain the best possible quality of life.
This choice should be discussed with the healthcare team and made based on the patient's wishes and priorities.
 Global Website
Global Website
 Home
Home